Arm Swelling: How to Reduce Swelling in Your Arm
Read More

Edema can lead to several symptoms, including edema bruising. People with edema typically bruise more easily, and those bruises may be accompanied by pain. Understanding the symptoms of edema and how to manage chronic swelling can help you control your symptoms and prevent complications. Here’s what you need to know about bruising from edema and what you can do to treat and manage symptoms.
What Is Edema?
What Causes Edema?
What Is a Bruise?
Can Edema Cause Bruising?
What Are Symptoms of Edema Bruising?
How Can You Treat and Manage Edema Bruising?
Key Takeaways: Managing Edema with Bruising
Edema is a medical condition caused by an excess of fluid in the tissue of the body that leads to swelling. Edema most commonly occurs in the legs and arms, but it can affect any area of the body, including the head, neck, groin, abdomen, and feet. The degree of swelling can vary and can last from a few days to several months or more.
Edema occurs when fluid leaks out of small blood vessels and into your body’s tissues, causing that fluid to build up and swell in the affected area. Measuring edema is an important part of getting the proper treatment. There are different stages of edema that can be measured by girth, volume, and the depth and duration of pitting. You can reduce the risk of advanced stages of edema by following an edema treatment and management plan.
There are several potential causes of edema, so getting a proper diagnosis is key. Understanding the cause of your swelling can help you get the treatment you need to manage your symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
Edema has several potential causes, which is why it’s crucial to get a proper diagnosis. In some cases, edema is caused by an acute injury and only lasts a few days. Chronic edema may be caused by a more serious underlying health condition, so you should see a doctor if your swelling doesn’t go away. Below are some of the common causes of edema:1
A bruise, also known as a contusion or black and blue mark, forms on your skin when blood collects beneath a layer of skin as a result of trauma. Bruises occur when you have an injury that causes your small blood vessels to break, allowing blood to leak out into the surrounding tissue. In many cases, bruises are accompanied by minor swelling as well as pain. Bruises change colors from a deeper red or purple color to a lighter yellow as the injury heals — this has to do with the amount of oxygen in the bruise and how the body breaks down blood.2
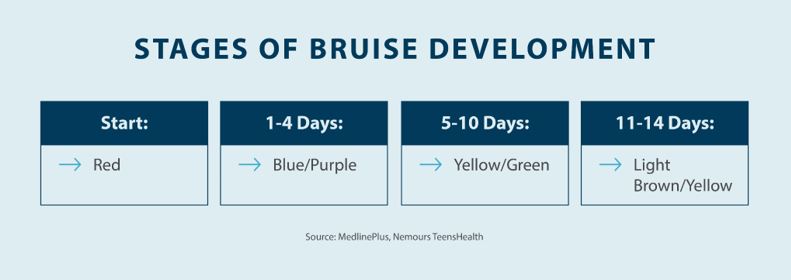
In many cases, bruises aren’t a cause for concern, as they typically go away in a few days to a couple of weeks and are the result of a minor injury, such as bumping into an object. In some cases, however, a bruise may last for several months and be the result of a more serious underlying health condition.
While skin bruises are the most common, muscle bruises and bone bruises can also occur. You may have bone bruising if you’re experiencing additional symptoms, such as a hard lump in the affected area and sharper pain, so you should seek advice from a doctor.
Certain medical conditions can make you more prone to bruising. If you bruise easily, you should try to avoid physical activities that may cause bruises.
Edema and bruising have a close relationship because of their effects on your body. Not only can edema make you bruise easily, but bruises can also cause edema.
When you have excess fluid in your body’s tissue as a result of edema, it puts more pressure on your blood vessels. This increase in pressure makes it easier for tiny blood vessels to rupture, which is how bruises occur. Because of this, people who have edema typically bruise more easily, which can lead to pain and tenderness in the area. This is also why you have to be extra careful about injuries if you have edema.
On the other hand, bruising can also lead to edema. As we explained earlier, bruises are a result of a ruptured blood vessel leaking blood into the surrounding area. When that fluid leaks into your body’s tissue, it can lead to swelling as a result. Swelling caused by bruising is typically temporary, and you can get relief by icing and elevating the bruised area.
Keep in mind that there are several blood-related conditions that make you bruise easily, such as hemophilia or vitamin deficiencies. If you notice bruises on your arms or legs and you’re not sure how they got there, you should visit a doctor to determine why you’re bruising so easily.
Recognizing the symptoms of edema with bruising can help you monitor your symptoms and minimize complications. There are a handful of symptoms that commonly present with an edema bruise, ranging from discoloration to pain and tenderness.

Some of the common symptoms that accompany bruising caused by edema include:
If you have edema, it’s important that you work with your doctor to figure out the best treatment plan. Whether you have a lymphatic disorder or edema caused by an acute injury, your doctor or specialist can help you create a plan to manage your symptoms and reduce the risk of your edema from progressing.
First and foremost, you should avoid activities that come with a high injury risk. If you live an active lifestyle, talk to your doctor about physical activities that are safe for edema patients.
If your edema is caused by an underlying health condition, treating that health condition is a key focus. Conditions like lymphedema, chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), and congestive heart failure can lead to edema bruising and severe swelling, so start by getting a proper diagnosis.
Maintaining a healthy weight is a big part of managing edema bruising and swelling. Regularly exercising can help reduce swelling caused by lymphedema, and it also helps with weight loss. A nutritious diet with a low salt intake can help prevent excess fluid retention.
Compression garments and devices are another effective way to reduce and prevent swelling caused by edema. You can wear compression socks or sleeves that your doctor prescribes, or you can try a pneumatic compression device like the Flexitouch Plus System or Nimbl System from Tactile Medical.
Manual lymphatic drainage is a massage technique that you can use to encourage lymphatic drainage. Ask your doctor or specialist about manual lymphatic drainage if you have lymphedema.
Edema bruising can have an impact on your daily life, which is why avoiding injuries is a key part of managing edema. Bruising can lead to edema and vice versa, so be mindful of physical activities that may cause injuries. You can talk to your doctor or edema specialist to learn more about managing edema and reducing bruising.
If you’re looking for relief from swelling, stiffness, and the pain that may accompany the bruising, Tactile Medical can help. The Flexitouch Plus System and Nimbl System give you targeted relief for swelling that you can use from the comfort of your home, allowing you to manage your symptoms and maintain your quality of life. Contact Tactile Medical to learn more about our solutions today.
References
1. InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-. Causes and signs of edema. 2008 Nov 5 [Updated 2016 Dec 30]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279409/
2. MedlinePlus. Bruises. MedlinePlus.gov. Accessed September 6, 2023. https://medlineplus.gov/bruises.html
Read More
Edema can affect any part of the body, but in some cases, it may only present itself in one leg. Edema in one leg is typically caused by a localized injury or lymphatic malformation that leads to swelling. Swelling in one leg can cause discomfort and affect your daily life,...
Read More
Measuring edema can help you get an accurate diagnosis. Learn how edema assessments are performed, along with treatment and other information, here.
Read More
Subcutaneous edema occurs in the deepest layer of skin and can cause swelling and other symptoms. Learn more about subcutaneous edema in this guide.
Read More
Call us at 1.833.3TACTILE (1-833-382-2845)