Peripheral Edema
Review our guide on peripheral edema to learn about its symptoms, causes, and treatment, so you can manage your condition.
Read More
Subcutaneous edema is swelling (edema) that happens in a specific layer of the skin. Subcutaneous edema is often connected to some form of tissue damage, which can result from another medical condition or an acute injury. Treatment is focused on mitigating the symptoms and swelling that result from this buildup of fluid. If you want to learn more about subcutaneous edema, what causes it, and how it’s treated, keep reading.
What Are the Three Layers of Skin?
What Is Edema?
What Is Subcutaneous Edema?
What Are the Symptoms of Subcutaneous Edema?
What Causes Subcutaneous Edema?
How Do You Treat Subcutaneous Edema?
Wrapping Up: Subcutaneous Edema
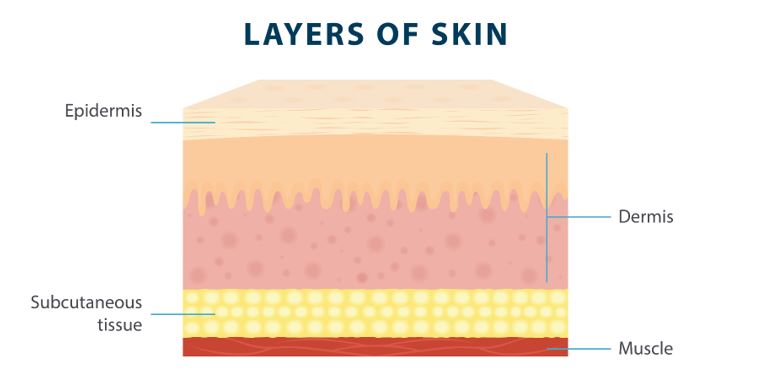
Your skin is made up of three layers: the epidermis, the dermis, and the subcutaneous tissue.

The epidermis is the outermost layer of skin, which is what most people think of when they think of skin. The epidermis is responsible for keeping germs and bacteria from getting into your body and causing infections. This layer of skin also gives your skin its color, makes new skin, and supports your immune system through Langerhans cells.1
The dermis is the middle layer of the skin, which is responsible for many of the functions of your skin. The dermis makes oil, grows hair, produces sweat, supplies blood to the epidermis, and more.1
The deepest layer of skin is known as the hypodermis, or the subcutaneous tissue. This is the layer of tissue that comes just before the muscle tissue, and it helps regulate your body temperature and protect your muscles and bones.1 Edema of subcutaneous tissue can affect its ability to perform its crucial roles.
Edema is a medical condition characterized by a buildup of fluid in the body’s tissues, resulting in swelling. Fluid levels in the body are typically regulated by your kidneys, lymphatic system, and other parts of the body. When the interstitial fluid in the body isn’t properly regulated, it can build up in the extremities and lead to swelling. This swelling may be accompanied by various symptoms, including pain and skin tightness.
While mild subcutaneous edema may not be a serious concern initially, untreated edema may lead to numerous complications. Edema that isn’t properly managed may eventually lead to blisters, ulcers, and infections, so it’s important to visit a doctor or specialist to figure out a subcutaneous edema treatment plan as soon as possible.
Subcutaneous edema is a specific type of edema that affects the hypodermis layer of skin. Because this deeper layer of skin plays so many important roles, subcutaneous edema can have a serious effect on blood vessels and nerves in the deeper layers of the skin.
One thing to keep in mind is that subcutaneous edema may be associated with other medical conditions, so visiting a doctor for diagnosis is crucial. Untreated chronic subcutaneous edema can lead to cellulitis that is often associated with this condition but is avoidable with proper treatment.
If you want to prevent edema blisters and other potential complications of subcutaneous edema, it’s important to be aware of the symptoms. If you experience any of these common subcutaneous edema symptoms, you should talk to a doctor or specialist about your treatment options:
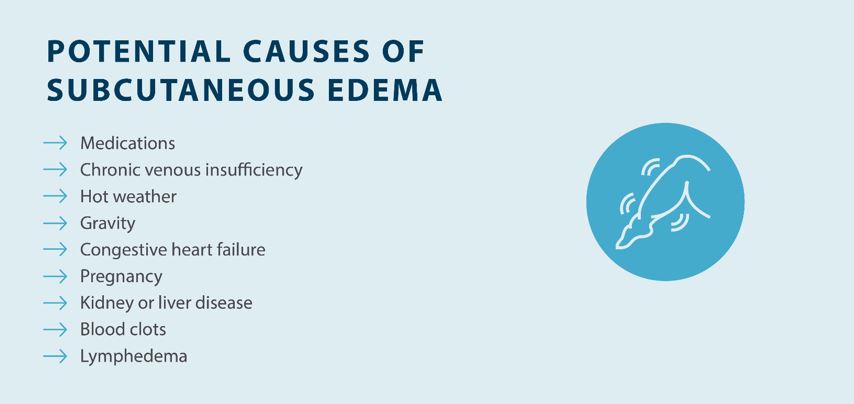
Like any type of edema, subcutaneous edema may be caused by a combination of lifestyle choices, genetics, medical conditions, and environmental factors. Here are some of the potential causes of subcutaneous edema:2
Before treating subcutaneous edema, it’s important to get a proper diagnosis first. Doctors will often perform a physical examination to identify any symptoms, such as pitting. They may also ask for a medical history and family history to determine if those are contributing factors. In some cases, your doctor may use tests, such as ultrasounds or other tests to rule out certain medical conditions and to diagnose subcutaneous edema. From there, they will work with you to create a treatment plan to help reduce swelling and the progression of symptoms. Here are some common treatments for subcutaneous edema:
Getting an early diagnosis for subcutaneous edema is essential to determine a treatment plan. Fortunately, subcutaneous edema can be managed with basic treatment, including compression, exercise, diet, and elevation.
Do you need help getting relief from swelling and other edema symptoms? The Flexitouch Plus system from Tactile Medical can help. If you want to learn more about the Flexitouch Plus and how it can help you reduce swelling, get in touch with Tactile Medical today.
References
1. Yousef H, Alhajj M, Sharma S. Anatomy, Skin (Integument), Epidermis. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470464/
2. Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Edema. 2008. https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/subcutaneous+edema
Review our guide on peripheral edema to learn about its symptoms, causes, and treatment, so you can manage your condition.
Read More
Read More
Edema can affect any part of the body, but in some cases, it may only present itself in one leg. Edema in one leg is typically caused by a localized injury or lymphatic malformation that leads to swelling. Swelling in one leg can cause discomfort and affect your daily life,...
Read More
Edema can lead to several symptoms, including edema bruising. People with edema typically bruise more easily, and those bruises may be accompanied by pain. Understanding the symptoms of edema and how to manage chronic swelling can help you control your symptoms and prevent complications.
Read More
Call us at 1.800.575.1900