Lymphedema and Weight Loss
Living with lymphedema while trying to manage your weight can feel overwhelming, but understanding the connection between lymphedema and weight loss can help you develop effective strategies for both conditions.
Read More
Living with stage 2 lymphedema brings unique challenges, but understanding your condition is the first step toward effectively managing it. While this stage marks a point where the condition becomes irreversible, there are many ways to maintain your quality of life and prevent symptoms from progressing.
Keep reading to explore everything you need to know about stage two lymphedema, from its symptoms and causes to diagnosis and treatment options.
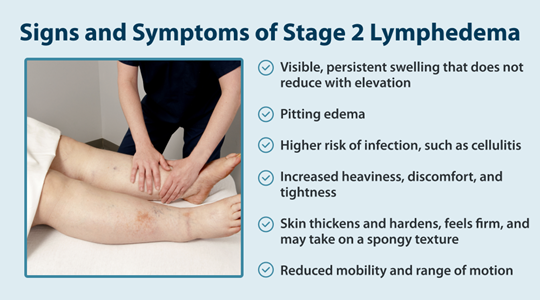
Stage 2 lymphedema is a significant point in the progression of this chronic condition, which affects the lymphatic system. Unlike stage 1, where swelling might come and go, and the condition can be reversed, the second stage of lymphedema brings more persistent changes. At this stage, the buildup of lymph fluid becomes more pronounced and doesn’t improve with simple elevation or overnight rest.1
When comparing stages of lymphedema, it’s helpful to understand the progression. Stage 1 typically shows temporary swelling that might go down with elevation. In stage two lymphedema, the swelling becomes more permanent, and tissues start to harden. If left untreated, it can progress to stage 3, where the skin undergoes significant changes and becomes even harder and more fibrotic. This progression risk makes it even more important to understand and properly manage stage 2 symptoms.1
Recognizing the signs of lymphedema at this stage is crucial for proper management. The symptoms of stage 2 lymphedema are more noticeable and consistent than earlier stages, making them key indicators for seeking treatment.2
Understanding the causes of lymphedema can help you better manage your condition and identify potential risk factors. The root causes typically fall into two main categories: primary and secondary.
Primary lymphedema occurs when genetic factors affect the development or function of the lymphatic system. It can appear at any age but is most common during times of hormonal changes, such as puberty. However, primary lymphedema can be congenital and present at birth due to lymphatic vessels not developing properly, while others may develop lymphedema later in life, known as lymphedema tarda.
Secondary lymphedema is more common and develops due to damage to or disruption of the lymphatic system. This often occurs after cancer, cancer surgery, radiation therapy, injury, or infection. Understanding lymphedema risk factors can help you identify if you might be at risk for developing this condition.2
You can only get an accurate diagnosis from a healthcare provider; lymphedema isn’t a condition you can diagnose on your own since it can sometimes be mistaken for other conditions. Healthcare providers use several methods to confirm stage two lymphedema and determine how to treat lymphedema with the best approach. A few ways your doctor might diagnose you with lymphedema are:2
Managing stage 2 lymphedema requires a comprehensive treatment plan. While the condition can’t be cured, proper treatment can help control symptoms and prevent complications. A few ways stage 2 lymphedema is treated include:

Living with stage 2 lymphedema requires dedication to your treatment plan, but you don’t have to face it alone. Working closely with your healthcare team helps ensure you take the right steps to manage your symptoms and prevent progression to stage 3. Regular monitoring, consistent care, and open communication with your healthcare providers create the foundation for successful long-term management.
For many people, at-home treatment options can make a significant difference in managing symptoms. Tactile Medical’s lymphedema products, including the Flexitouch Plus and Nimbl systems, offer doctor-prescribed pneumatic compression devices that can be used at home. These systems can complement your overall treatment plan, helping you maintain better control over your symptoms while fitting treatment into your daily routine.
References:
1. “Lymphedema Stages.” Breastcancer.Org – Breast Cancer Information and Support, Breastcancer.org, 15 Aug. 2023, www.breastcancer.org/treatment-side-effects/lymphedema/stages.
2. Greene, Arin K, and Jeremy A Goss. “Diagnosis and Staging of Lymphedema.” Seminars in Plastic Surgery, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Feb. 2018, pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5891654/.
Living with lymphedema while trying to manage your weight can feel overwhelming, but understanding the connection between lymphedema and weight loss can help you develop effective strategies for both conditions.
Read More
Stage three lymphedema is the most advanced stage of this chronic condition. In this stage, the affected body part might display one or more symptoms, such as significant swelling, alterations in the skin, or recurring episodes of infection. While this stage can be challenging to manage, understanding your condition and...
Read More
When the lymphatic system becomes compromised, fluid buildup can lead to stage 1 lymphedema, a condition marked by mild but noticeable swelling in affected areas. This initial stage is a crucial window for intervention, as proper treatment can prevent progression to more severe stages. Knowing the signs, causes, and treatment...
Read More
Read More
Call us at 1.800.575.1900