Lymphedema Guide: What Is Lymphedema?

Lymphedema is a progressive disease where an abnormal amount of fluid accumulates in a localized region of the body. This excess fluid typically occurs in an arm or leg, but can also occur anywhere in the body such as the head and neck as well as the chest, abdomen, or genitals. The lymphatic system is often referred to as the main filter for waste products in the body such as toxins, fat, and cancer cells. When the lymphatic system becomes damaged or congested due to lymph node removal or damage to lymph vessels, it can no longer successfully perform its job of filtering toxins and waste from a specific part of the body and this results in swelling, known as lymphedema.
Lymphedema can be painful and uncomfortable and can lead to more serious health conditions if left untreated, such as trouble with mobility, an increased risk of developing a skin infection, and permanent changes in your skin. If you notice your leg or arm is chronically swollen, consult your doctor to get an accurate diagnosis.
In this blog post, we will define lymphedema and outline its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
-
What Is Lymphedema?
What Is the Lymphatic System?
What Are the Stages of Lymphedema?
What Can Cause Lymphedema?
What Are Lymphedema Signs and Symptoms?
Can You Prevent Lymphedema?
How Is Lymphedema Diagnosed?
Complications of Lymphedema
What Are Lymphedema Treatments?
What Is the Life Expectancy of Someone With Lymphedema?
Key Takeaways: What Is Lymphedema?
What Is Lymphedema?
Lymphedema refers to an accumulation of fluid or swelling. The lymphatic system that drains this fluid is located just under the skin. Lymph fluid is the part of the lymph system that transports cells that fight infections in the body. Lymphedema is caused by a blockage of the lymphatic vessels, which leads to fluid retention and swelling.
Lymphedema can either be primary or secondary. Primary lymphedema can be inherited or present at birth, while secondary lymphedema is caused by an injury or obstruction of the lymphatic system. Primary lymphedema is rare and affects about 1 in 100,000 individuals, and can develop at any point in your life. Secondary lymphedema is more common, affecting roughly 1 in 1,000 Americans, and is typically the result of damage or injury to the lymph nodes or vessels such as trauma, chronic venous insufficiency, cancer, or cancer treatment.
What Is the Lymphatic System?
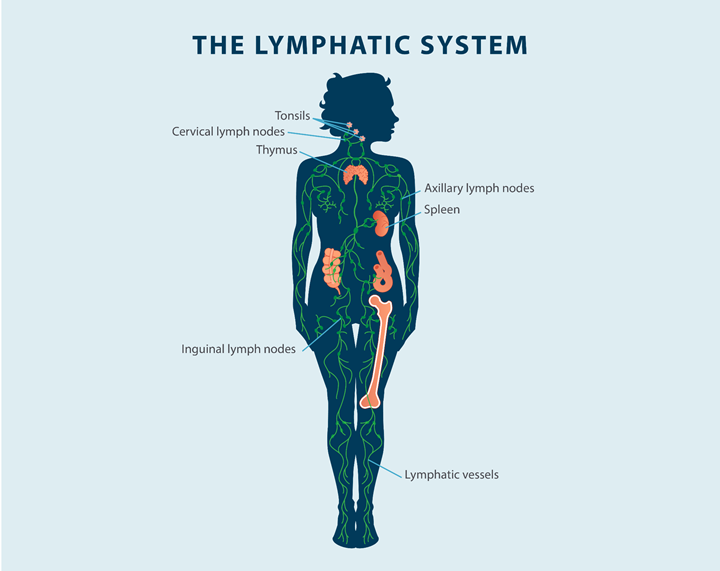
The lymphatic system is a large network of lymph nodes, vessels, and organs that move lymph fluid throughout the body tissues back to the circulatory system. This network is part of your body’s immune system, and it helps filter and rid the body of toxins and waste. Lymph fluid is made up of fat, water, protein, cellular debris, and lymphocytes that are white blood cells, which help fight bacteria in the blood, and a fluid called chyle, which is found in the intestines.
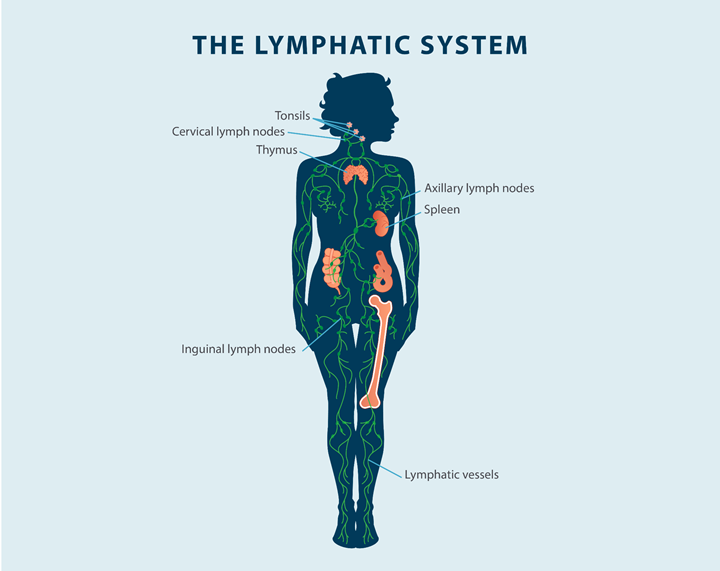
The lymphatic system includes the bone marrow, spleen, lymph nodes, thymus, and lymphatic vessels. The lymphatic vessels spread throughout all the tissues of the body.
Lymph nodes create immune cells, which help the body fight off infections. Lymph nodes also filter the lymph fluid to remove bacteria and cancer cells from the body. If bacteria or cancer cells are found in the lymph fluid, the lymph nodes will create more white blood cells to fight off the infection. Lymph nodes are located in different areas of the body, such as the neck, armpit, abdomen, and groin.
What Are the Stages of Lymphedema?
Lymphedema is categorized into four different stages, depending on what your swelling looks like, where it’s occurring, and how it’s progressing.
The four stages of lymphedema are:
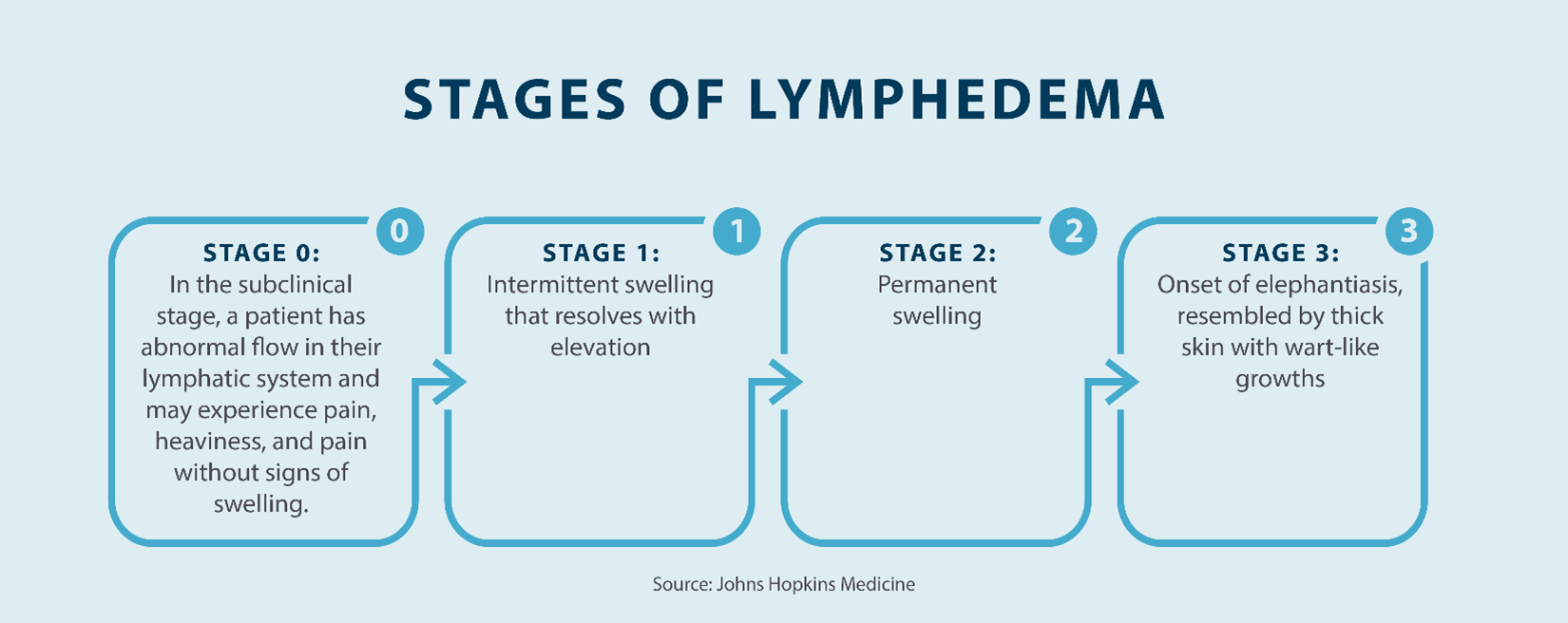
- Stage 0: In the first stage of lymphedema, which is referred to as the latent or subclinical stage, there is an abnormal flow in the lymphatic system, but swelling is not visible. This stage can continue for months or years without you even noticing symptoms. However, you may experience feelings of achiness, heaviness, and pain, so it’s very important to keep note of any symptoms in the affected area to see if they worsen over time.
- Stage 1: The second stage of lymphedema is called the mild stage. During this stage, slight swelling will start to occur in the affected area. The skin in this area will look puffy, and you may experience “pitting edema,” which is when an indentation is left on the skin after pressure is applied. Swelling during this stage can be reduced by elevating the affected area.
- Stage 2: The third stage is called the moderate state, and this is when the swelling doesn’t improve despite elevating the affected area. Pitting will most likely go away as excess fat begins to form and tissue fibrosis develops. The skin will continue to swell, and scarring and thickening may form.
- Stage 3: The last stage of lymphedema is called the severe stage, and it’s when the most amount of swelling forms. During this stage, the skin begins to thicken, and the tissue becomes hard. More changes in the skin will start to occur, such as hyperpigmentation. Fat deposits and wart-like growths may also develop, along with elephantiasis and permanent damage. During this stage, the skin is most susceptible to infection.
Treating your lymphedema as early as possible is imperative to preventing further symptoms, infections, and skin fibrosis. The key to living with lymphedema is learning ways to manage it, and staying consistent with a treatment routine. This consistency can help you avoid some of the later-stage symptoms that lymphedema can cause.
What Can Cause Lymphedema?
Understanding the cause of lymphedema can help with your diagnosis and treatment options. Some of the potential causes of lymphedema include:
- Cancer: Lymphedema is a common result of cancer. This is because cancer cells can block your lymph vessels, which can result in swelling.
- Obesity: Obesity can cause lymphedema, as excess fat can put pressure on lymphatic vessels and nodes, inhibit lymphatic drainage, and cause swelling.
- Surgery: Certain surgeries, such as cancer surgery, can also lead to lymphedema. If the lymph nodes are removed to prevent cancer from spreading, this can cause the fluid to build up in the surrounding tissues, which can lead to swelling.
- Radiation treatment: Radiation treatment for cancer can also cause lymphedema. Certain radiation treatments can damage the lymph vessels and result in scarring or inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- Traumatic event: Any kind of traumatic event, such as a sports injury, car accident, work accident, or deep cut, can result in lymphedema if the lymph nodes and vessels are damaged.
- Vascular diseases: Vascular diseases, such as chronic venous insufficiency or blood clot, can lead to poor circulation of fluids in your body, resulting in the swelling of lower extremities like your legs, feet, and ankles.
What Are Lymphedema Signs and Symptoms?
Lymphedema symptoms can come on suddenly, or they may develop over time. You should keep an eye on your symptoms to see if they change or worsen.
Some of the potential symptoms of lymphedema include:
- Swelling or discomfort: The affected area will be swollen and feel uncomfortable. The swelling will likely be intermittent and slight at first but increase over time.
- Numbness: Numbness, tingling sensations, and a tight feeling in the skin on the affected area are common symptoms of lymphedema.
- Loss of mobility: Depending on how severe your swelling is, you may experience a loss of range of motion, mobility, or pain while moving the affected area.
- Heavy feeling: The affected area will feel heavy and uncomfortable to move.
- Pitting: If you press on the skin in the affected area and an indentation is left, that means you have pitting edema. Pitting is a common side effect of lymphedema.
- Infection in the area: Infection in the affected area is possible. Signs of infection will include fever and warmth, tenderness, redness, and pain around the swelling.
- Clothing or jewelry feels tighter: If your clothing, shoes, or jewelry starts to feel tighter on your skin, that can be a sign of lymphedema.
If you notice any of these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately. Even if the swelling isn’t present at first, it’s possible that your symptoms will progress and lead to more serious health complications.
Can You Prevent Lymphedema?
While lymphedema can’t be fully prevented, there are various steps you can take to reduce your chances of developing it or stop it from escalating, such as:
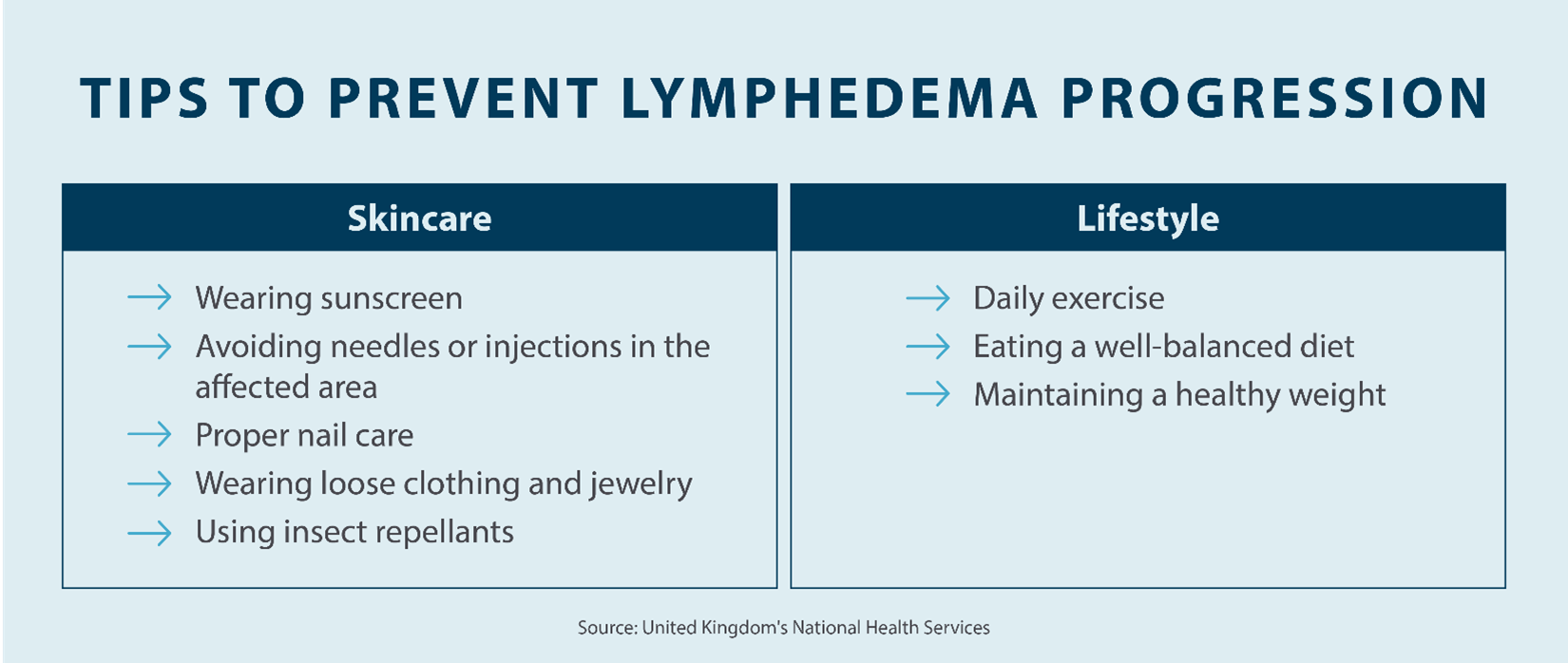
- Prioritize your skincare: Taking better care of your skin can help mitigate the symptoms of lymphedema, as the skin in the affected area is more vulnerable to infection. Any cuts in your skin mean bacteria can enter, which can lead to infection. Take the following steps to help prevent worsening symptoms:
- Treat any cuts or burns immediately
- Avoid hot tubs
- Moisturize the skin in the affected area daily
- Use insect repellent to prevent bug bites
- Wear sunscreen
- Live a healthy lifestyle: A healthy and well-balanced lifestyle can also lower your chances of developing lymphedema. This can also help to stop it from escalating into a more serious condition. Living a healthy lifestyle means eating a well-balanced diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight. The healthier you are, the better your body can fight off infections, and the less likely you’ll be to develop lymphedema.
How Is Lymphedema Diagnosed?
If you suspect you may have lymphedema, it’s important to see a doctor so that you can get a proper diagnosis. Your doctor will have the best idea if what you’re suffering from is lymphedema, and can prescribe the appropriate course of treatment to help you manage symptoms.
Your doctor will likely begin by performing a thorough examination to rule out a more serious condition, such as kidney disease or congestive heart failure. Once you have received a diagnosis of lymphedema, your doctor may order a lymphoscintigraphy to conform the diagnosis. This is a safe assessment, which involved a tiny injection of radioactive dye into your veins to show how the lymph fluids move throughout your body. They may also do an MRI or a CT scan to show where exactly the swelling is taking place. An ultrasound may also be conducted to help find any obstructions that may be causing the swelling.
Complications of Lymphedema
There are various complications that can result from lymphedema, which is why it’s important to get the swelling treated as soon as symptoms arise.
Some of the potential complications of lymphedema include:
- Deep vein thrombosis, also known as a blood clot
- Skin infections from bacteria
- Lymphangitis, which is the inflammation of the lymphatic vessels (channels)
- Functional impairments, such as decreased range of motion or loss of mobility
- Post-surgery complications, such as:
- Seroma, which is a build-up of encapsulated fluid
- Hematoma, also known as bruising
- Skin necrosis, which is the death tissue
- Partial wound separation
- Sepsis, which is when the infection enters the blood stream which can be life-threatening.
- Skin changes, such as hyperpigmentation, wart-like lesions, or hardening of the skin
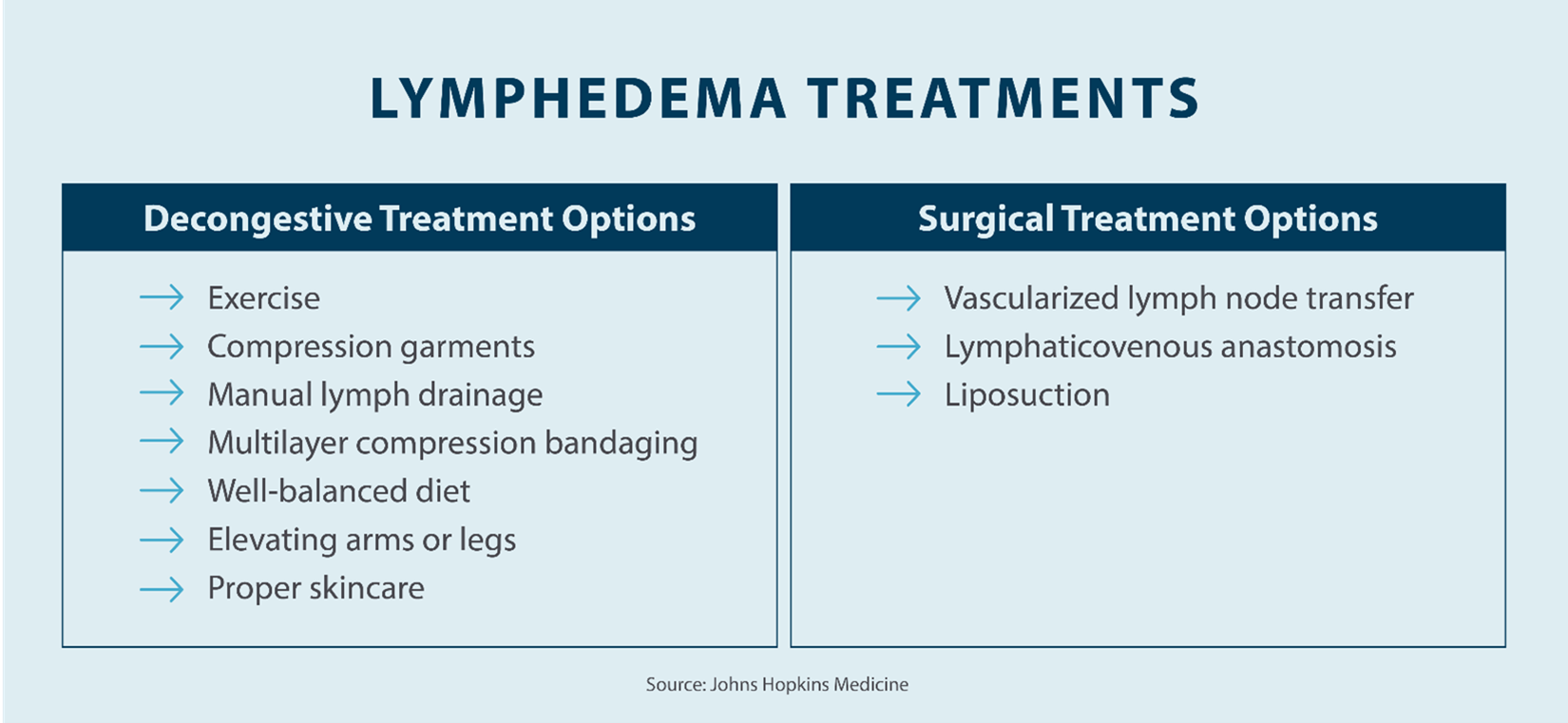
What Are Lymphedema Treatments?
Lymphedema treatment will look different for everyone, depending on what part of your body is affected and how severe your symptoms are. In addition to taking the right steps to prevent your lymphedema from worsening, it’s also important to find the right course of treatment.
A professional lymphedema therapist can provide decongestive therapy. Through decongestive therapy, your therapist will perform a specific type of massage that redirects the flow of fluids away from the swollen region to reduce swelling. A therapist may also provide instructions of how to perform decongestive therapy massage techniques, known as manual lymphatic drainage (MLD), that you can perform at home, along with other forms of at-home treatments, such as:
- Exercise: Exercising regularly helps to improve flexibility and strength, which can encourage drainage of the lymph fluid.
- Wear compression garments: Your doctor may recommend wearing a compression garments such as compression stockings, multi-layer bandages, or other compression garments to prevent the build-up of fluid.
- Elevate the affected area: In the beginning stages of lymphedema, elevating the affected area can help to reduce swelling. Keeping the area raised gives gravity the chance to drain the lymph fluid.
- Use a lymphedema pump: Using a lymphedema pump can help to increase the flow of lymph fluid and keep the fluids from accumulating in the affected area.
Daily maintenance is essential to treating your lymphedema and living a healthy and happy life. Lymphedema pumps, also called pneumatic compression devices, fit over extremities that are affected by lymphedema, such as your arms and legs. Then, an air pump fills the device chambers with air which applies a gentle pressure to move excess fluid and relieve symptoms. Using a lymphedema pump is a great way to alleviate symptoms of lymphedema right from your home. Another component of treatment is compression bandages, which help reduce the amount of fluid and prevent it from refilling or building up.
In some cases of lymphedema, your doctor may recommend surgical treatment. Surgical treatment is more common in the latter two stages, but can be performed in earlier stages. if surgery is needed, procedures can include:
- Vascularized lymph node transfer (VLNT)
- Lymphaticovenous anastomosis (LVA)
- Liposuction
To prevent lymphedema from progressing to more severe stages, it’s important to take preventative measures, such as treating and managing symptoms from the start. At Tactile Medical, our at-home lymphedema solutions can help you alleviate discomfort, relieve pain, and improve mobility challenges.
In addition to the above treatment methods, there are various other ways to treat lymphedema at home, such as with Tactile Medical’s lymphedema pumps. Tactile Medical’s lymphedema treatment recommendations include following a prescribed treatment with your pump to reduce swelling and encourage the flow of lymph fluid. Tactile Medical has compression pumps for every area of the body, including the upper body, lower body, and head and neck.
If you have swelling in your lower body, upper body, or your head and neck, Tactile Medical’s pneumatic compression device gently assists in the drainage of excess fluid through a dynamic work and release action.
What Is the Life Expectancy of Someone With Lymphedema?
Lymphedema is a life-long disease, but in most cases, it’s not life-threatening as long as you take the right steps to treat it. Consult with your doctor to determine the best treatment options for you. At Tactile Medical, our lymphedema pumps can be prescribed by your doctor and don’t involve the need for medications or surgery.
Key Takeaways: What Is Lymphedema?
If you notice any swelling in your arm or leg, it may be a sign of lymphedema. If left untreated, it can lead to more serious health concerns, such as pain, discomfort, and infection, which is why seeking help from a doctor or lymphedema specialist is important.
Lymphedema is swelling that’s caused by an accumulation of lymph fluid in your body. It can affect any part of your body, and the swelling can happen immediately or over time. The swelling can be painful and uncomfortable and can make doing your daily tasks more difficult. With lymphedema, doing something as simple as getting up in the morning to go to work can become a challenge.
Fortunately, there are many ways you can treat and manage lymphedema. If you’re in the beginning stages, making simple healthy lifestyle changes and keeping the affected area elevated can help to relieve symptoms. Maintenance therapy solutions, such as Tactile Medical’s lymphedema products, the Flexitouch Plus System and Entre Plus System, can assist in the home management of lymphedema symptoms like chronic swelling and venous ulcers. In later stages, surgery may be recommended to reduce swelling and encourage the flow of lymph fluid. The type of treatment you’ll need depends on the severity of your swelling.
Tactile Medical provides pneumatic compression pumps that can be used to treat lymphedema symptoms right at home. We offer garments to use with the pump for the upper body, lower body, and head and neck. No matter where your swelling is, Tactile has a solution for you so you can reduce your swelling and go back to living a healthy and happy life.