Inflammation vs Swelling
Review our guide on the differences between inflammation vs. swelling, so you can understand how they impact your body differently.
Read More
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) affects millions of adults, yet many don’t fully understand this progressive vascular condition. When your leg veins can’t effectively pump blood back to your heart, you may experience uncomfortable symptoms like swelling, pain, and visible skin changes.
This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about chronic venous insufficiency, from recognizing early warning signs to understanding available treatment options that can help you manage this condition and, in turn, improve your quality of life.
Chronic venous insufficiency is a condition that describes when the veins in your legs can’t efficiently return blood to your heart. Under normal circumstances, your leg veins work against gravity with the help of one-way valves and muscle contractions to push blood upward and back to the heart for recirculation. However, for individuals living with chronic venous insufficiency, the valves become weakened or damaged, causing blood to flow backward and pool in the lower legs.1
This condition affects approximately 10% to 35% of adults, with prevalence increasing significantly with age.2 Women experience chronic venous insufficiency more frequently than men, particularly after pregnancy or during hormonal changes. The condition becomes more common after the age of 50, although it can develop at any age, depending on individual risk factors.1
Understanding how chronic venous insufficiency differs from other swelling conditions helps clarify the diagnosis and treatment. Lymphedema is a chronic, progressive condition that involves the lymphatic system’s inability to drain fluid properly. While venous disease impacts venous circulation, lymphatic insufficiency presents when chronic venous insufficiency progresses, requiring both the veins and lymphatics to be treated.
Lipedema is another chronic and progressive condition, characterized by symmetrical fat distribution in the legs and arms. For lipedema patients, chronic venous insufficiency is a common comorbidity, as the increased pressure and inflammation caused by abnormal fat accumulation can overwhelm the lymphatic and venous systems.
Chronic venous insufficiency progresses through seven distinct stages. Healthcare providers use this staging system to determine the most appropriate treatment approaches and monitor progression.1,2

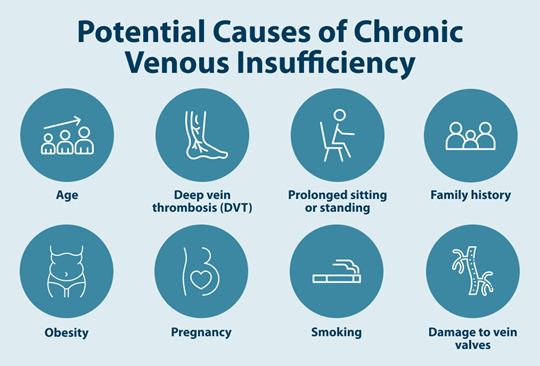
Multiple factors can contribute to chronic venous insufficiency, often working in combination to weaken the vein walls and damage the delicate valves that prevent blood from backing up. Common chronic venous insufficiency causes include:1,3
Chronic venous insufficiency symptoms typically develop gradually and may initially be subtle enough to be overlooked or attributed to other causes. Recognizing these symptoms early can help you get the necessary treatment before the condition progresses.1,2
Diagnosing chronic venous insufficiency begins with a comprehensive medical evaluation that combines your symptom history with physical examination findings. Your healthcare provider will ask about when symptoms occur, what makes them better or worse, and whether you have risk factors for venous disease.
During the physical examination, your doctor will carefully inspect your legs for visible signs of chronic venous insufficiency, including varicose veins, swelling, skin discoloration, and any open wounds. They may also feel for areas of tenderness or check how quickly swelling rebounds when pressed.
The most important diagnostic tool for chronic venous insufficiency is ultrasound, a painless imaging study that evaluates blood flow patterns and vein structure. This test uses sound waves to create detailed images of your leg veins, measuring both the direction and speed of blood flow.1
Chronic venous insufficiency treatments aim to improve blood flow, reduce symptoms, prevent complications, and enhance quality of life. The most effective approach typically combines multiple treatment strategies tailored to your specific situation and disease severity. Options include:1
Chronic venous insufficiency isn’t a life-threatening condition, and people with this diagnosis can expect normal life expectancy with proper management. However, the condition is progressive, meaning symptoms typically worsen over time without appropriate treatment. With consistent care that includes compression therapy, lifestyle modifications, and medical treatments when needed, most people maintain an excellent quality of life.
Unfortunately, chronic venous insufficiency cannot be completely reversed because the underlying valve damage is permanent. However, this doesn’t mean you’re without options for feeling better. The condition is indeed progressive, but following a comprehensive treatment protocol can significantly slow its advancement and dramatically reduce symptoms.
Several home management strategies can significantly improve chronic venous insufficiency symptoms and slow disease progression. The treatments for swelling include:
Early detection and proactive treatment of CVI can make a significant difference in your life. If you’re experiencing symptoms that might indicate chronic venous insufficiency, don’t wait to consult with a healthcare provider. They can perform the necessary evaluations to confirm the diagnosis and work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan.
For those requiring advanced compression therapy, Tactile Medical’s Flexitouch Plus and Nimbl systems offer doctor-prescribed pneumatic compression devices that can significantly improve symptom management as part of a comprehensive treatment approach.
References
1. “Chronic Venous Insufficiency: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment.” Cleveland Clinic, Jul 22 2025, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16872-chronic-venous-insufficiency-cvi.
2. Patel SK, Surowiec SM. Venous Insufficiency. [Updated 2024 Feb 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430975/
3. “Chronic Venous Insufficiency.” Johns Hopkins Medicine, Aug 8 2021, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/chronic-venous-insufficiency.
Review our guide on the differences between inflammation vs. swelling, so you can understand how they impact your body differently.
Read More
The lymphatic system helps our body fight diseases and infections. Find out more about the lymphatic system and its functions in this guide.
Read More
Lymphatic circulation is a key part of the immune system. Learn more about the role of the lymphatic system in the body.
Read More
When your lymphatic system isn’t functioning properly, fluid can build up in your body tissue and lead to swelling. Lymphedema is a medical condition characterized by swelling that can make life more difficult due to pain, decreased mobility, and other symptoms. Fortunately, there are several ways you can manage your...
Read More
Call us at 1.800.575.1900