What Causes Lymphedema

Lymphedema is a condition that occurs when fluid builds up in a part of your body, causing pain, swelling, and discomfort in the affected area. Lymphedema causes vary but typically occur when there’s a disruption to the lymphatic system.
One of the most common causes of lymphedema is when lymph nodes are removed during surgery for cancer, which can cause swelling in the areas associated with those nodes. Another cause of lymphedema can be a vascular disease, such as chronic venous insufficiency or deep vein thrombosis, resulting in swelling in a limb. Throughout this post, we’ll go into more detail about lymphedema causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Use the links below to navigate the post or read end-to-end for an in-depth look at the causes of lymphedema.
What is lymphedema?
Lymphedema is a term used to describe localized swelling in the body caused by an abnormal accumulation of lymphatic fluid. Lymphedema can occur anywhere in the body, such as the head, neck, arms, legs, chest, abdomen, and genitals. The lymphatic system consists of lymph vessels, nodes, and organs, which have a role in fluid balance, immunity, and fat transport. The system transports fluid from the body’s tissues back to the central circulation, so damage to the system can lead to an accumulation of fluid in that area.
When lymphatic fluid builds up in the tissue in one part of your body, it causes swelling. This swelling can lead to pain and discomfort in the affected area, and it can get worse if you don’t take steps to reduce the swelling. Keep in mind that there are different lymphedema treatment and management options based on where the swelling occurs.
Diagnosing lymphedema requires the help of a doctor because there are other conditions that can cause swelling and pain in a limb. The diagnosis of lymphedema is often established through patient history and a physical examination. However, your doctor may choose to use other tests to provide imaging of the venous and lymphatic systems. These tests commonly include ultrasound, but some providers may also use NIRF lymphatic imaging, lymphoscintigraphy, CT scans, or MRI scans. Getting a proper diagnosis is important because it rules out other potential causes of pain and swelling and allows you to focus on lymphedema treatment options.
Unlike some conditions that lead to swelling and pain, lymphedema is chronic. If you’re living with lymphedema, it’s important to focus on ways to improve comfort, reduce swelling, and relieve symptoms. Treating your lymphedema as early as possible is imperative to preventing further symptoms, infections, and skin fibrosis.
What Can Cause Lymphedema?
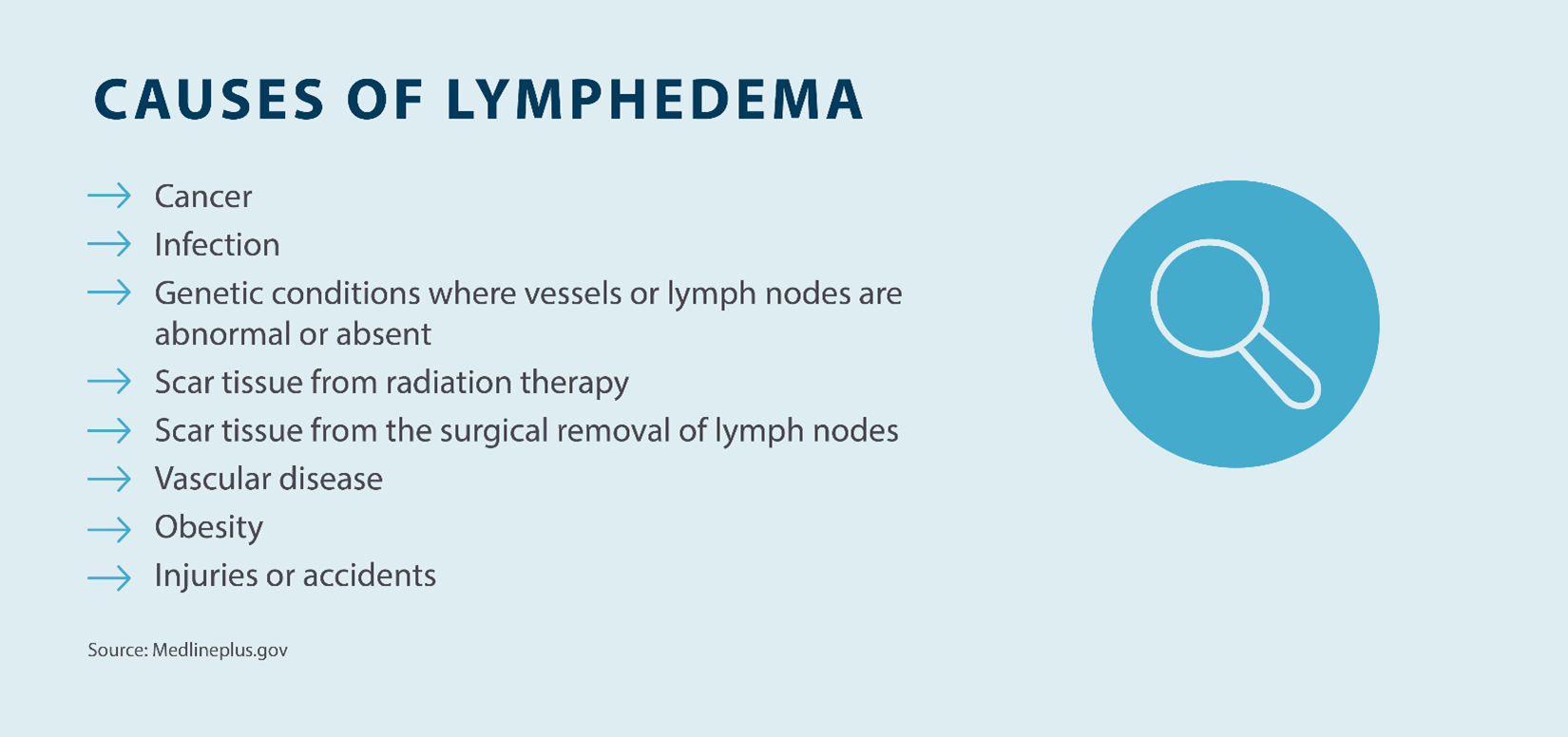
Lymphedema can be caused by several factors, making it difficult to determine what resulted in your diagnosis. Your body has a network of vessels and lymph nodes that are used to carry lymphatic fluid from the body’s tissues back to the central circulation. The lymph nodes work to filter out bacteria, toxins, and cellular waste. When lymphatic nodes or vessels are damaged, the flow is impaired, and the fluid accumulates.
One of the most common causes of lymphedema is surgery to remove a cancerous tumor and/or lymph node removal to prevent cancer spread. Anyone who has this type of surgery is at risk for developing lymphedema due to this insult or impairment to the lymphatic system. The patient may develop swelling after surgery that does not resolve, or may develop swelling months or even years later. However, it’s important to note that this doesn’t always result in lymphedema, so you may not experience lymphedema as a result of cancer-related surgery.
Radiation treatment is another common form of cancer treatment and can cause damage to both your lymph nodes and vessels, resulting in scarring and inflammation. This damage can impair the lymphatic flow, resulting in lymphedema.
Vascular disease is another common cause of lymphedema, mostly affecting the lower extremities, including the feet, ankles, and lower legs. Common vascular conditions, such as chronic venous insufficiency, vasculitis, and deep vein thrombosis, can disrupt the natural drainage of lymphatic fluid. As a result, swelling of the lower extremities can occur, along with pain and discomfort.
Obesity can also cause lymphedema. When there is excess adipose tissue (fat), it can place pressure on your body’s lymphatic nodes and vessels. In turn, this can decrease or prevent lymphatic draining, which can result in swelling. By maintaining a healthy weight, you can reduce and prevent lymphedema symptoms.
An abnormality in the formation of the lymphatic system, such as malfunctioning or missing lymph nodes or vessels, can also lead to lymphedema. These hereditary conditions can be present at birth, or infancy, or appear around the time of puberty, or later in adulthood. This type of lymphedema is called primary lymphedema. Swelling can appear in one or more limbs, the face, abdomen, or genitals.
Lastly, trauma can cause lymphedema. Your lymphatic system is close to your skin’s surface, and trauma, such as a crushing injury, car accident, or burn, can cause damage to your lymphatic vessels and nodes, which can lead to lymphedema and swelling.
What Are Lymphedema Symptoms?
While the causes of lymphedema vary, the symptoms remain the same for most people. Early symptoms of lymphedema include sensations of heaviness, tightness, tingling, warmth, or pain. These symptoms may come and go for a period of time before there is noticeable swelling. For most people, swelling is the most bothersome symptom and is the reason most people decide to visit a doctor.
As lymphedema gets more severe, it can lead to other problems in the affected limb. You may notice that the fluid-filled limb feels increasingly heavy or tight, which is a result of the pressure caused by the fluid building up. In some cases, you might even lose a significant amount of range of motion in a limb, making it difficult to walk or use your arm. With lymphedema in an extremity, you can also experience a loss of mobility.
As for head and neck lymphedema, symptoms can include swelling of the eyes, face, neck, and lips, along with difficulty moving your neck, shoulders, or jaw. Other potential symptoms of head and neck lymphedema can include congestion, earaches, and trouble breathing, eating, or speaking. If you’re experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to visit a doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment plan.
Lymphedema can also lead to symptoms that you might not think would be related to the condition. For example, that buildup of fluid in the same limb can eventually lead to hardening of the skin, which is known as fibrosis. Some people who suffer from lymphedema may experience frequent, recurring infections resulting from problems within their lymph system. Because the lymphatic system is an important part of your body’s defense against infections, damage to lymph nodes or lymph vessels can cause a weakened immune system.

It’s important to understand that these symptoms can worsen if left untreated. The key to living with lymphedema is learning ways to manage it, and staying consistent with a treatment routine. This consistency can help you avoid some of the later-stage symptoms that lymphedema can cause. Seeking guidance from an expert is always recommended.
How Do You Treat Lymphedema?
If you’ve been diagnosed with lymphedema, your primary focus should be finding lower body lymphedema treatment and upper body lymphedema treatment options, such as compression bandages and pneumatic compression devices, also known as lymphedema pumps. These at-home solutions can help you reduce swelling and improve the symptoms associated with lymphedema. A certified lymphedema specialist can help diagnose lymphedema and offer management solutions to treat your symptoms.
A lymphedema specialist will recommend lifestyle changes, such as an increase in exercise and stopping smoking, if applicable. The therapist can provide decongestive therapy and teach manual lymphatic drainage techniques (MLD) to redirect fluid from swollen areas.
Lymphedema specialists will suggest meticulous skincare. You should clean the arm or leg that’s affected by lymphedema and apply lotion to it daily. While it’s important to thoroughly dry your skin after cleaning it, make sure you’re gentle to prevent damaging the skin. You should take care of your fingernails to avoid scratches, and avoid cutting your cuticles to prevent infection. If you have a cut, make sure you clean it with soap and water right away to prevent infection.
Since lymphedema causes swelling, reducing that swelling is key. You can reduce swelling by wearing compression stockings or sleeves. Consult with a doctor before doing so. You should also keep the affected limb elevated as much as possible, and avoid putting too much stress on it.
The Flexitouch Plus system from Tactile Medical is clinically proven to stimulate your lymphatic system to reduce the symptoms of lymphedema. There are garments designed for lower body, upper body, and head and neck Flexitouch therapy. This is a safe treatment that doesn’t involve medications or surgical procedures and can be prescribed by your physician. The Flexitouch is an at-home management solution, clinically-proven to reduce swelling, relieve pain, and improve the lymphatic flow in affected extremities.
Wrapping Up: Lymphedema Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Sudden swelling can be caused by a variety of health conditions, so it’s important to visit a doctor if you’re experiencing swelling that won’t subside. If your swelling is caused by lymphedema, you should talk to your doctor about which treatment options are best for you and what you can do to manage your lymphedema.
When it comes to managing lymphedema, Tactile Medical can help. If you’re looking for a non-surgical treatment option that doesn’t require taking medication, the Flexitouch Plus system can help you manage lymphedema in the head, neck, arms, or legs. The Flexitouch Plus system is designed for at-home use, so you can reduce symptoms associated with lymphedema and help prevent its progression. Ask your doctor today if the Flexitouch Plus system is right for you.